Delserro Engineering Solutions (DES) is excited to announce the addition of advanced, state-of-the-art package test equipment focused on enhanced testing to our already extensive range of testing capabilities. Our commitment to staying at the forefront of technological advancements enables us to provide our clients with comprehensive and cutting-edge testing solutions that cater to the diverse requirements of various industries.
Our continuous investment in new package test equipment allows us to expand our capacity and meet the growing needs of our clients in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, consumer goods, electronics, medical devices, and more. By combining our decades of expertise in testing services with the latest equipment, we ensure that our clients receive accurate, reliable, and efficient solutions for all their packaging needs.
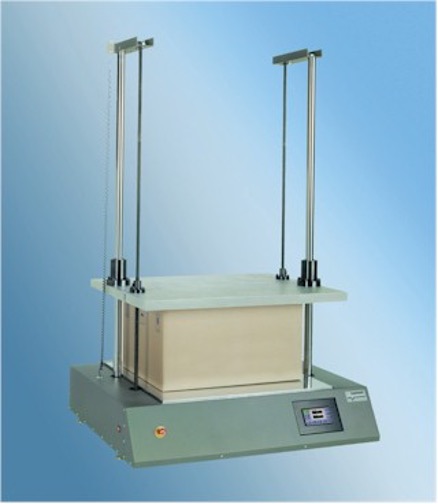
The Vibration Tester: Ensuring Package Performance
One essential component of our testing arsenal is the vibration tester, which enables us to assess a package’s performance under various vibration conditions. With the help of our advanced vibration tester, we can identify potential weaknesses in the packaging and ensure that products remain protected during transportation and handling.
DES understands that each industry and client has unique packaging challenges, and our expanded testing capabilities allow us to customize our services to meet these specific requirements. Whether your focus is on improving durability, ensuring product safety during transportation, or meeting strict regulatory standards, our state-of-the-art package test equipment and experienced team of engineers are here to help you achieve your goals.
ASTM D4169 and Other Industry Standards for Package Testing
DES is committed to meeting and exceeding industry standards for package testing. The new package equipment, including the Lansmont Squeezer Compression Test System, is designed to perform compression testing in accordance with ASTM D642, ASTM D4169, and TAPPI T804. By adhering to these established guidelines, DES is committed to providing testing services that meet the highest levels of quality and reliability. For more information on these standards, see our frequently asked questions (FAQ) section below.
In addition to enhancing our existing services, the new package test equipment also allows us to explore innovative testing methods and stay ahead of emerging trends in the packaging industry. Our commitment to continuous improvement ensures that we not only meet the current demands of our clients but also anticipate and address future challenges.
Ready to ensure your packaging meets industry standards? Request a quote today and speak with our experts to discuss your package testing project.
Expanding our Package Test Equipment Portfolio
DES has recently added two cutting-edge pieces of package test equipment to our lineup: the Lansmont PDT 80 package drop tester and the Lansmont Squeezer.
The Lansmont PDT 80 Precision Drop Tester can test packages weighing up to 177 lbs., with a drop height range of 12 to 72 inches. Capable of performing flat, edge, and corner drops, the package drop tester meets the requirements of ASTM D5276 and ISO 2248.
The Lansmont Squeezer Compression Test System is specifically designed to perform compression testing on packages, including constant load tests that simulate long-term warehouse stacking. Featuring a platen size of 30 x 30 inches and a maximum opening of 48 inches, the Squeezer boasts a force capability of up to 5,000 lbs.
In addition to the new Lansmont package test equipment, DES has an altitude chamber and multiple temperature/humidity chambers to simulate various environmental conditions during testing.
DES offers ASTM and ISTA Package Testing services within our environmentally controlled, accredited laboratory. For more information on our package testing capabilities or to discuss your package testing project with one of our experts, please contact us or call 610.253.6637. Our team is committed to providing exceptional testing services to ensure the utmost quality and reliability of your packaging solutions.
Package Testing Standards FAQ
What is the ASTM?
ASTM stands for the American Society for Testing and Materials, now known as ASTM International. It is a globally recognized organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, and services. ASTM standards are used across various industries to improve product quality, enhance safety, facilitate market access and trade, and build consumer confidence.
These standards are developed through a consensus process involving volunteers from various industries, governments, academia, and consumers who work together in technical committees to create and maintain the standards. ASTM International’s standards are widely used and accepted worldwide, serving as a common language for industries and helping to ensure quality, safety, and interoperability.
What is ASTM D642?
ASTM D642 is a standard test method for determining the compressive resistance of shipping containers, components, and unit loads.
What is ASTM D4169-16?
ASTM D4169-16 is a standard practice for performance testing of shipping containers and systems, evaluating their ability to withstand various distribution hazards.
What is the ASTM D4169 method?
The ASTM D4169 method is a practice for performance testing of shipping containers and systems, using a sequence of tests to simulate real-world conditions such as handling, transportation, and environmental exposure.
What is the difference between ASTM D4169-22 and D4169-16?
ASTM D4169-22 and D4169-16 are different versions of the same standard, with the -22 and -16 indicating the year of revision. There may be updates or changes in the testing procedures, equipment, or requirements between the two versions.
What is the difference between ASTM D4169-14 and -16?
ASTM D4169-14 and -16 are different versions of the same standard, with the -14 and -16 indicating the year of revision. The differences may include updates or changes in the testing procedures, equipment, or requirements.
What is the difference between ASTM D4169-16 and ISTA 3A?
ASTM D4169-16 is a standard practice for performance testing of shipping containers, while ISTA 3A is a test protocol from the International Safe Transit Association (ISTA) that focuses on packaged products weighing 150 lbs. (68 kg) or less. Both are designed to evaluate packages’ performance but use different test sequences and may have different specific requirements.
What is the sample size for ASTM D4169?
The sample size for ASTM D4169 varies depending on the type of container or packaging system being tested. The standard provides guidance on selecting representative samples, but it does not prescribe a specific number of samples to test.
What is the difference between ASTM D4169 and ISTA 1A?
ASTM D4169 is a comprehensive standard practice for performance testing of shipping containers and systems, while ISTA 1A is a test protocol from the International Safe Transit Association (ISTA) that focuses on packaged products weighing up to 150 lbs. (68 kg) under non-simulation integrity testing. ASTM D4169 covers a wider range of distribution hazards, whereas ISTA 1A is more focused on basic integrity testing, specifically vibrations and impacts.



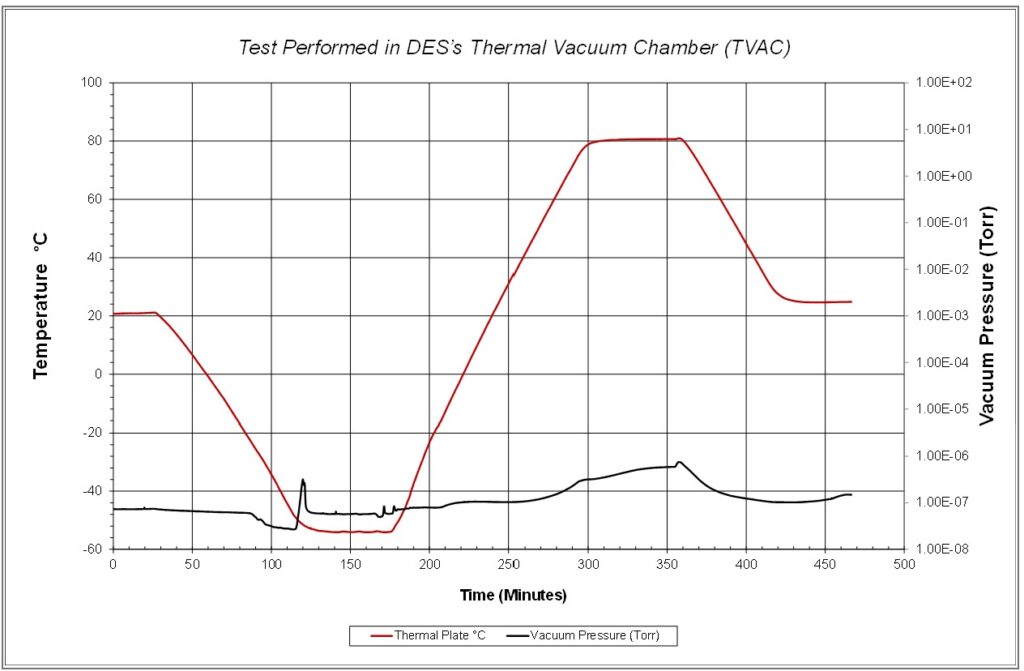


 Delserro Engineering Solutions (DES) was proud to recently perform testing for the NASA Psyche Program. More information about this program can be found at the following web link
Delserro Engineering Solutions (DES) was proud to recently perform testing for the NASA Psyche Program. More information about this program can be found at the following web link